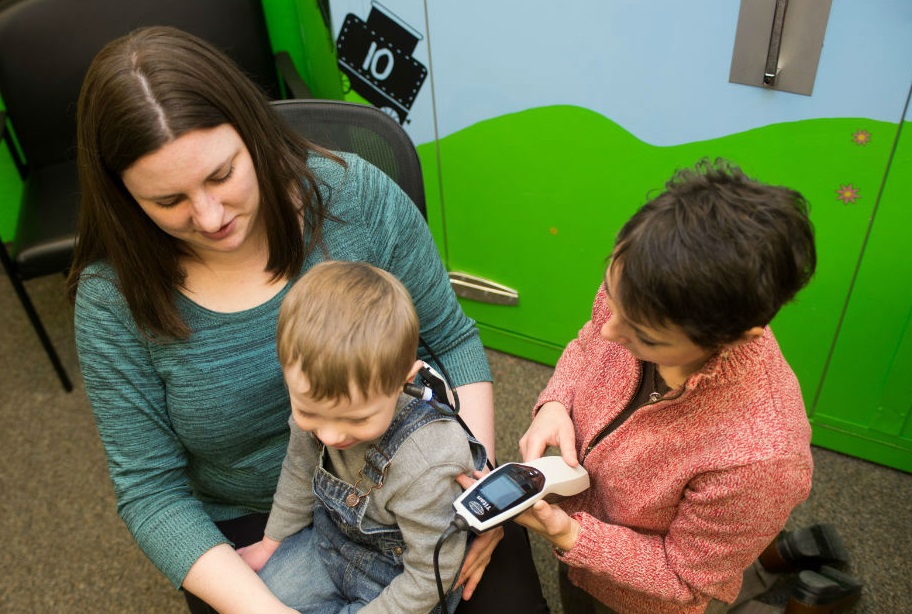
ISU Audiology Clinic, Pocatello
CONTACT US:
650 Memorial Dr., Bldg. 68
Pocatello, ID 83209
Phone: (208) 282-3495
Fax: (833) 390-1293
HOURS:
Monday - Friday
8:30 AM - 3:00 PM
(Hours for all services including canine vary due to academic calendar)
ISU's Audiology Clinic provides quality audiology services including: comprehensive evaluations, hearing screenings, and hearing aid device implementation for adults and children in the community and surrounding areas, ISU faculty, staff, students, and United States Veterans. Our Audiologists have a variety of specialized backgrounds including: balance function testing, cochlear implants and bone anchored hearing aids, auditory processing difficulties, assistive learning devices, amplification, and hearing conservation.
Idaho State University recognizes that our mission is to care, support, and educate individuals and families affected by health conditions that diminish their quality of life. We acknowledge that individuals may experience discrimination in the healthcare system, which can adversely affect their health outcomes. We recognize that both conscious and unconscious discrimination occur. Overt and conscious discrimination is not tolerated. Unconscious or unintentional discrimination need to be identified, challenged, and addressed. We believe everyone has the right to be healthy and have access to the resources they need.
We strive to achieve the following commitments to our colleagues and our patients:
- Goal 1: We do not discriminate on the basis of age, race, ethnicity, religion, culture, language, physical or mental disability, socioeconomic status, sex, sexual orientation and gender identity or expression.
- Goal 2: All patients receive the highest level of care possible delivered in a patient and family friendly approach using evidence-based medicine.
- Goal 3: We recognize racism, not race, as the cause for healthcare disparities and therefore will examine our healthcare treatment plans for bias.
- Goal 4: We will track information on factors that create disparities as they relate to health outcomes to better identify how we may actively seek to eliminate such disparities in healthcare.
- Goal 5: We intend to improve the diversity of our workforce to reflect the community we serve.
- Goal 6: We commit to listen, learn, and seek to understand in order to create impactful and sustainable positive change.
- Goal 7: We will recognize and reward practices that promote health equity.
Definition of health equity: The state in which everyone has a fair and just opportunity to attain their highest level of health. https://www.cdc.gov/
While the terms equity and equality may sound similar, the implementation of one versus the other can lead to dramatically different outcomes for marginalized people: Equality means each individual or group of people is given the same resources or opportunities. Equity
Hearing Services
Hearing evaluations help determine what kind of hearing loss you may have by measuring your ability to hear sounds. A licensed audiologist supervising a Doctor of Audiology student will perform a hearing evaluation using an audiometer to determine your hearing sensitivity at different frequencies.
What can I expect at my Hearing Evaluation?
The hearing evaluation will begin with a review of the areas that you are experiencing hearing difficulty, questions about your symptoms, history of noise exposure, and other medical history. A combination of the following tests may be given to determine your hearing sensitivity:
- Otoscopy: This is a physical examination of the outer ear, the ear canal, and the eardrum using a light.
- Pure Tone Audiometry: This is an evaluation to determine your hearing levels and can also help determine the type, degree, and configuration of hearing loss.
- Bone Conduction: This evaluation can determine if a hearing loss is conductive (related to problems in the outer or middle ear) or sensorineural (the result of inner ear or auditory nerve dysfunction).
- Word Recognition: This evaluation will determine if you can hear speech at a louder level and how well you can distinguish words.
- QuickSIN (Quick Speech in Noise): This will evaluate your ability to separate speech from background noise.
- Tympanometry: This evaluates the middle ear system through using pressure to move the eardrum and small bones behind the eardrum.
- Acoustic Reflex: This evaluation measures a muscle contraction in the middle ear in response to loud sounds.
Hearing Device Selection, Fitting, and Counseling
Your audiologist has recommended that you would benefit from the use of hearing devices. The process of improving your quality of life is just beginning. Your audiologist will guide you in the selection of hearing devices appropriate for your hearing loss and listening needs. A hearing health management plan that incorporates your unique lifestyle and listening needs will be used to identify the best hearing solution. Once a hearing solution has been selected, you will return for a hearing device fitting at which point the hearing devices will be programmed to your hearing loss and tested to insure that they are functioning appropriately in your ear. Hearing devices work the best when they are on your ears and being worn so you will also be shown how to care for your hearing devices. You will also learn how to care for your hearing aids such as:
- Making adjustments for different environments;
- Inserting and removing the devices;
- Communication strategies;
- Battery care; and
- Cleaning and maintenance.
A few weeks after your initial visit, a follow-up visit will be scheduled to determine if any adjustments may be required to improve your device functioning.
Hearing Device Styles
Hearing devices come in a wide range of sizes, technology features, and accessories. Hearing devices range from completely in the canal to devices which sit behind the ear. Your audiologist will help guide you towards an appropriate style that fits your lifestyle and listening needs.
Choosing the Right Hearing Device
Hearing aids, as with any technology, are constantly changing. No one technology fits everyone. Our clinic has access to hearing devices from major manufacturers and can work with you to determine which hearing aid style and features are appropriate for you hearing loss and listening needs. In determining the appropriate hearing devices, we will examine the following criteria:
- Degree of hearing loss: Your degree of hearing loss determines which speech sounds you may or may not be able to hear without the assistance of a device. The degree of hearing loss may determine the style of hearing device that can be worn.
- Ear configuration: The shape of the ear may determine which hearing device is most appropriate. For example, someone who has had ear surgery may not be able to wear hearing aids that sit behind the ear.
- Manual controls: The majority of hearing devices are automatic and will adjust depending on the environment; noise, speech, music, etc. Certain manual controls may be needed depending on the wearers lifestyle and listening needs.
- Wireless connectivit: Many hearing devices can now connect to and be controlled wirelessly through Bluetooth® devices or applications on a smartphone. Other wireless accessories for help in hearing the television, landline telephone, and speakers from a distance are also available.
- Dexterity and Visual acuit: As technology has improved, hearing devices have become smaller Every hearing device takes a battery, requires the user to place the device in their ear, and requires regular cleaning and maintenance. Some hearing device styles are easier to manipulate than others and may be recommended based on visual acuity and dexterity.
Hearing Device Maintenance and Repair
Just as with any electronic technology, hearing devices require cleaning and maintenance to keep them in working condition. The enemies of hearing devices are moisture, ear wax, dust and dirt. With daily care and maintenance, hearing devices should last between 5-7 years. There are several ways to care for your hearing devices and most devices will come with cleaning supplies or can be purchased through the ISU Audiology Clinic. A soft cloth can help remove oils from the skin and any debris such as dead skin and wax. Avoid using water or alcohol pads as this can damage the hearing aids. Hearing aids should be stored in a dry safe place away from children or pets. Every 4-6 months it is best to visit the ISU Audiology Clinic for a deep hearing aid cleaning to keep your hearing aids in optimal working condition.
If your hearing aids are not working despite your cleaning efforts, hearing aids can be dropped off at the front desk of the ISU Audiology Clinic and processed through the Hearing Aid Repair Clinic.
Hearing Device Troubleshooting
Feedback is the squealing sound that your hearing aid sometimes makes.
- Check for wax in the microphone or receiver opening.
- Make sure your earmold is fitting snugly.
- Feedback may also occur if there is excess cerumen in the ear. If you feel that this may apply to you, call our clinic for an appointment to have it removed.
No sound from the hearing aid
- The battery may be dead.
- Wax or other debris can block the opening on the microphone or receiver causing the hearing aid to not function appropriately.
Hearing Device Accessories
Hearing devices often have the ability to connect to or be used in conjunction with other accessories to help the user hear the television, a cell or landline phone, and in difficult-to-hear situations.
- Bluetooth and wireless technology: remote controls, cell phone applications, television headsets, wireless microphones, allow the user to hear in areas of hearing difficulty.
- FM transmitters and receivers are often used in classroom settings in order to hear the person speaking such as a teacher and reduce background noise or the distance sound must travel between the speaker and the hearer.
- Assistive Listening Devices
Hearing Device Supplies
- Batteries: typically batteries last 7-10 days. Hearing device batteries can be purchased at pharmacies and grocery stores and typically cost $1.00 per battery. It is best to keep a few spare batteries on hand. These can be purchased from the ISU Audiology Clinic.
- Wax guards: These filters or guards help prevent wax from entering the electronic components of hearing aids. These can be purchased from the ISU Audiology Clinic.
- Cleaning kits: Brushes, wax removal tools, and battery magnet are a few of the cleaning tools contained in cleaning kits. These can be purchased at the ISU Audiology Clinic.
- Dry-aid kits: These are dehumidifying boxes which work to pull moisture from the hearing device. Individuals who sweat, work outside, or live in humid environments benefit from storing their hearing devices in a dry-aid kit. These can be purchased from the ISU Audiology Clinic.
Custom Earmolds, Swim Plugs, and Custom Hearing Protection
Depending on the style of your hearing devices, custom earmolds may be needed and an impression of your ear will be taken. This can ensure a good fit in the ear canal. This process takes 10 minutes and then the impression will be sent to a manufacturer to be made into a custom earpiece.
Custom swim plugs are a great way to prevent moisture that can aggravate the outer ear and ear canal. While no swim mold can create an absolutely watertight seal in the ear canal, a custom swim plug can reduce water and other irritants from entering the ear.
Custom hearing protection for hunters, shooters, and those in noisy industries provides a more comfortable and secure fit than over-the-counter products. Musician’s plugs are custom fit but also filtered to maintain the fidelity of music while still protecting hearing.
The ISU Audiology Clinic provides audiological services to pediatric patients of all ages from the community and surrounding rural areas. Our audiologists specialize in pediatric hearing evaluations and treatment for children with hearing loss. Our pediatrics services include newborn, infant, preschool and school ages hearing screenings as well as diagnostic assessments. A typical evaluation consists of a complete behavioral test battery which may include Visual Reinforced Audiometry (VRA), Conditioned Play Audiometry (CPA) and standard puretone testing which is supplemented with tympanometry, acoustic reflexes, and Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) as appropriate. Also the audiologists perform auditory brainstem response (ABR) and Auditory Processing (APD) evaluations.
If a hearing loss is diagnosed, treatment options are available. Hearing aid selection and services are provided for our pediatric patients as well as parent education and counseling, bone anchored devices and cochlear implants. At ISU we utilize resources and programs to help provide hearing aids for children who are unable to access hearing devices.
Newborn Hearing Evaluation
The Audiology Clinic works in conjunction with Portneuf Medical Center to provide newborn hearing evaluations for babies born in the hospital and at home. The program follows the Idaho Sound Beginnings guidelines for infant testing. Initial testing and follow-up screenings, if needed, are provided in the hospital using ABR. Babies who do not pass or those who have high risk factors are seen in our clinic for a diagnostic hearing evaluation.
Salmon, ID Clinic
Dizziness and Balance
The ISU Balance Clinic offers vestibular testing and rehabilitation for patients suffering from vertigo, dizziness, visual disturbance, and/or imbalance. The clinic is staffed by audiologists and physical therapists working together to assess and treat the patient. Many times the underlying cause of the dizziness is a disagreement among the three main systems controlling our balance; vestibular function (inner ear), proprioception, and vision. A thorough evaluation of the dizzy patient often includes evaluation of ALL of these systems to determine how the brain organizes the information to maintain balance. The audiology and physical therapy programs at ISU have formed a transdisciplinary clinic for the purpose of evaluating dizziness and balance. Students and clinic supervisors see each patient at the same time. This approach allows each discipline to learn from the other; collaborate on the evaluation of a patient; and provide the patient with high-quality care.
Electrophysiology
This specialty clinic utilizes Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) testing for diagnostic auditory function testing on infants, children, and adults. Electrodes places on the head can determine how the hearing nerve is responding to a sound stimulus. A Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP) is used to evaluate two of the inner ear balance organs (the utricle and the saccule) and determine if the vestibular nerve is functioning appropriately. Electrodes are placed on the neck and sound is played in the ears and the response from the organs and nerve are measured to determine if they are functioning normally.
Cochlear Implants
The Cochlear Implant Clinic offers services to individuals who already have an implant and those considering implantation. Cochlear implant services include:
- Implant candidacy evaluations and consultations;
- Assistance and mapping with equipment upgrades for Advanced Bionics and Cochlear Corporation products;
- Troubleshooting and repairs of devices and accessories;
- Internal device impedance checks and map adjustments;
- Individualized auditory and speechreading training with options for individualized speech and language therapy;
- Support services for educational team members, teachers, parents and other family members.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus affects approximately 25 million Americans. It is most commonly described as “ringing in the ears” but it can also sound like roaring, clicking, hissing, or buzzing. It can affect both ears or just one ear. Tinnitus is usually a symptom of an underlying condition in the patient’s auditory system but could also be caused by a number of other conditions such as:
- Noise-induced hearing loss;
- Ear and sinus infections;
- Diseases of the heart or blood vessels;
- Thyroid abnormalities.
Sometimes Tinnitus can also be a side-effect of certain medications. Tinnitus is a common symptom of age-related hearing loss and loud noise exposure. There is no cure for Tinnitus but there are some management strategies that may give relief:
- Hearing devices;
- Counseling;
- Wearable sound generators;
- Environmental sound generators and phone apps;
- Acoustic neural stimulation;
- Cochlear implants.
Hearing Conservation
The ISU Audiology Clinic has partnered with local businesses to provide hearing conservation services consistent with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations. Employees are seen at the clinic for annual hearing tests as required by their employer which may also include education of employees regarding hearing loss and prevention of hearing loss, and compliance with rules and regulations set forth by OSHA as they relate to hearing conservation programs.
Community Hearing Screenings
A hearing screening is performed to determine if someone may have hearing loss. The screening is a quick, easy, and cost effective way to determine if a person needs a diagnostic evaluation. ISU Audiology travels onsite to perform hearing screenings at health fairs and community outreach events.
Canine Audiology Testing
In cooperation with the Veterans Administration Medical Center in Salt Lake City, Utah, our clinic provides hearing and hearing aid related services to the veterans living in southeast Idaho. This includes hearing evaluations, hearing aid evaluations, fitting state-of-the-art hearing aids, hearing aid orientation, fitting assistive devices, and counseling.
Our clinic is a contracted Community Care Network Provider working directly with the VA, HealthNet, and TriWest.
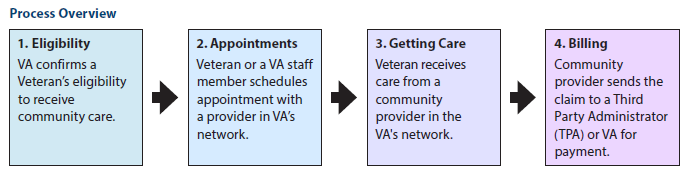
Community Care Network (CCN)
The VA CCN is the VA’s direct link with community providers to ensure Veterans receive timely, high-quality care. Under the new CCN, VA staff will refer Veterans directly to community providers and will directly schedule community care appointments for Veterans through the local VAMC. Veterans can also choose to schedule their own appointment with support from local VA staff.
Make an Appointment
Call (208) 282-3495 to schedule an audiology appointment:
- Pocatello Clinic Hours: Monday - Friday, 8:30 AM - 3:00 PM (Hours vary due to academic calendar)
- Canine Screening Hours: Friday, 11:00 AM - 3:00 PM (Hours vary due to academic calendar)
- Salmon Clinic Hours: By appointment only, 2 days per month, usually the last Thursday and Friday of the month
Call (208) 282-2590 to schedule a balance clinic appointment:
- Balance Clinic Hours: Monday - Wednesday, 8:30 AM - 11:00 AM
Patient Referrals
The ISU Audiology Clinic accepts referrals via phone or fax:
- Phone: (208) 282-3495
- Fax: (833) 390-1293
Referrals are required for all Medicare and Medicaid patients.
Parking
Patients can park in the areas designated “Clinic Patient Parking” or anywhere else in the reserved parking lot next to Bldg. 68. Parking passes are generally sent to the patient prior to visits, but can also be obtained from the staff at the clinic entrance.
Consent Forms
Consent forms are traditionally sent via DocuSign to your email account. If you are unable to sign consent forms electronically, paper copies are also available for your convenience. Please print and return with you on the day of your appointment.
Curtis Billings, PhD, CCC-A
(833) 390-1293
Dr. Billings provides comprehensive diagnostic audiology services.

Jeff Brockett, EdD, CCC-A
Associate Professor
(833) 390-1293
Dr. Brockett provides comprehensive diagnostic audiology services and specializes in balance evaluations.

Jennifer Holst, AuD, CCC-A
Program Director and Clinical Professor
(833) 390-1293
Dr. Holst provides comprehensive audiology services including hearing evaluations and hearing aid fittings for all ages. Dr. Holst specializes in pediatric audiology and auditory brainstem response (ABR) evaluations.

Chris Sanford, PhD, CCC-A
Associate Professor
(833) 390-1293
Dr. Sanford provides comprehensive diagnostic audiology services for all ages and specializes in middle ear assessment.

Deborah Vieira, MS, CCC-A
Clinical Assistant Professor
(833) 390-1293
Ms. Vieira provides comprehensive audiology services including hearing evaluations and hearing aid fittings for all ages. Ms. Vieira specializes in auditory processing disorder (APD) evaluations.
Staff
- Becca Rasmussen
Patient Care Coordinator
(208) 282-3495
fdaudiology@health.isu.edu
Billing
If you have insurance, please bring your insurance card with you to your appointment. Our clinic accepts and contracts with the following insurance plans:
- Aetna
- Ampliphon Hearing
- Blue Cross of Idaho
- Cigna
- Medicare
- Medicaid
- Pacific Source
- Regence Blue Shield of Idaho
- Select Health
- Tricare
- TriWest (with VA authorization)
- United Healthcare
- UHC Hearing
- UMR
Insurance Patients: The clinic accepts private insurance including Medicare and Medicaid. Medicare and Medicaid patients must have a physician referral in order for the clinic to bill your insurance. If you do not have a physician referral, you will be responsible for the billed charges if they are denied by your insurance company. All private insurance will be verified prior to your visit and a minimum payment of $50.00 is required at the time of service as most hearing benefits are not covered until the deductible has been met.
VA Patients: We participate in the Veteran's Patient Centered Community Care Program. This program allows Veteran's to access services outside of their local VA when those services are not readily available. The patient must contact the VA to access a referral, once that referral is obtained and an authorization has been issued, our office will schedule an appointment. We cannot accept patients without a valid authorization from the VA.
Payment
Most hearing services are non-covered and may be subject to your deductible.
- NOW ACCEPTING CARE CREDIT for Hearing Aids! Click here to apply.
- Statements are mailed monthly. Monthly payments are required to avoid collections. If you cannot pay your bill in full, monthly payment plans are available.
- Payment, including co-pays, is expected at the time of service.
- We accept cash, check, and visa/debit payments.
- Ask about our income-based sliding scale
- Click here to make an online payment:
No Surprise Billing Act
- Idaho Department of Health & Welfare
- American Academy of Audiology: The American Academy of Audiology is the world’s largest professional organization of, by, and for audiologists. The active membership of more than 12,000 is dedicated to providing quality hearing care services through professional development, education, research, and increased public awareness of hearing and balance disorders.
- American Speech and Language Association (ASHA): ASHA is the national professional, scientific, and credentialing association for more than 173,070 members and affiliates who are audiologists, speech-language pathologists, speech, language, and hearing scientists, audiology and speech-language pathology support personnel, and students. Audiologists specialize in preventing and assessing hearing and balance disorders as well as providing audiologic treatment, including hearing aids. Speech-language pathologists identify, assess, and treat speech and language problems, including swallowing disorders.
- American Cochlear Implant Alliance: The American Cochlear Implant (ACI) Alliance is a not-for-profit organization created with the purpose of eliminating barriers to cochlear implantation by sponsoring research, driving heightened awareness, and advocating for improved access to cochlear implants for patients of all ages across the United States.
- American Society for Deaf Children (ASDC): ASDC is a national organization of families and professionals committed to educating, empowering, and supporting parents and families of children who are deaf or hard of hearing. The ASDC helps families find meaningful communication options, particularly through the competent use of sign language, in their home, school, and community.
- Association of Late-Deafened Adults, Inc. (ALDA): ALDA serves as a resource center providing information and referrals, self-help, and support groups for people deafened as adults. ALDA works to increase public awareness of the special needs of deafened adults.
- Association of Medical Professionals With Hearing Losses (AMPHL): AMPHL aims to assist those in the professional health fields address issues surrounding their hearing loss. To help achieve this goal, their website provides information based on current issues in health fields along with personal experiences and insights into making hearing loss more compatible with the medical profession.
- Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA): HLAA provides assistance and resources for people with hearing loss and their families to learn how to adjust to living with hearing loss. Its national support network includes an office in the Washington, DC, area as well as 14 state organizations and 200 local chapters.
- American Tinnitus Association: ATA is a global leader in the effort to find a cure for tinnitus. We bring together patients, researchers, healthcare professionals, industry partners and lawmakers to develop tinnitus management tools and fund vital tinnitus research.
- Vestibular Disorders Association: VEDA provides information and support to the parents or teachers of people suffering from inner-ear balance disorders.
- Idaho Sound Beginnings: Early Hearing Detection and Intervention sponsored by the Department of Health and Welfare.
- Hands and Voices: A non-profit organization lead by parents who want to support families of children who are deaf or hard of hearing.